#Association of Publishers in India
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Emerald Spectacles from India, c. 1620-1660 CE: the lenses of these spectacles were cut from a single 300-carat emerald, and it was believed that they possessed mystical properties

These eyeglasses are also known by the name "Astaneh-e ferdaws," meaning "Gate of Paradise," based on the symbolic associations between the color green and the concept of spiritual salvation/Paradise. That symbolism (which is rooted in Islamic tradition) was especially popular in Mughal-era India, where the spectacles were made.

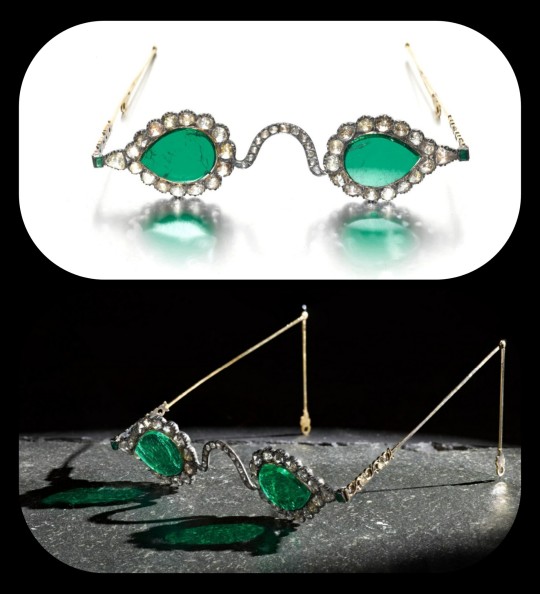
The lenses were crafted from two thin slices of the same emerald. Together, the lenses have a combined weight of about 27 carats, but given the precision, size, and shape of each lens, experts believe that the original emerald likely weighed in excess of 300 carats (more than sixty grams) before it was cleaved down in order to produce the lenses. The emerald was sourced from a mine in Muzo, Colombia, and it was then transported across the Atlantic by Spanish or Portuguese merchants.
Each lens is encircled by a series of rose-cut diamonds, which run along an ornate frame made of gold and silver. The diamond-studded frame was added in the 1890s, when the original prince-nez design was fitted with more modern frames.
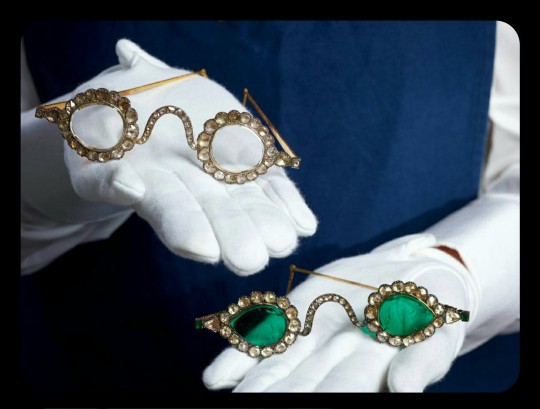

The emerald eyeglasses have long been paired with a second set of spectacles, and they were almost certainly commissioned by the same patron. This second pair is known as "Halqeh-e nur," or the "Halo of Light."
The Halo of Light features lenses that were made from slices of diamond. The diamond lenses were cleaved from a single stone, just like the emerald lenses, with the diamond itself being sourced from a mine in Southern India. It's estimated that the original, uncut diamond would have weighed about 200-300 carats, which would make it one of the largest uncut diamonds ever found.
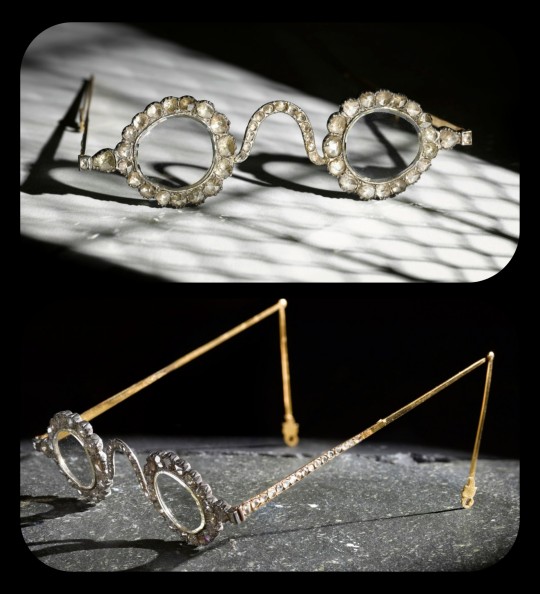

The lenses are so clear and so smoothly cut that it sometimes looks like they're not even there.
Both sets of spectacles date back to the mid-1600s, and it's generally believed that they were commissioned by a Mughal emperor or prince. The identity of that person is still a bit of a mystery, but it has been widely speculated that the patron was Shah Jahan -- the Mughal ruler who famously commissioned the Taj Mahal after the death of his wife, Mumtaz Mahal. Shah Jahan did rule as the Mughal emperor from about 1628 to 1658.
The emerald and diamond lenses may have been chosen for symbolic, sentimental, and/or cultural reasons, or they may have been chosen simply because they're pretty and extravagant; the original meaning and purpose behind the design is still unclear. Experts do believe that the eyeglasses were designed to be worn by someone, though.
At times, it was believed that the spectacles had spiritual properties, like the ability to promote healing, to ward off evil, to impart wisdom, and to bring the wearer closer to enlightenment. Those beliefs are largely based on the spiritual significance that emeralds and diamonds can have within certain Indic and Islamic traditions -- emeralds may be viewed as an emblem of Paradise, salvation, healing, cleansing, and eternal life, while diamonds are similarly associated with enlightenment, wisdom, celestial light, and mysticism.
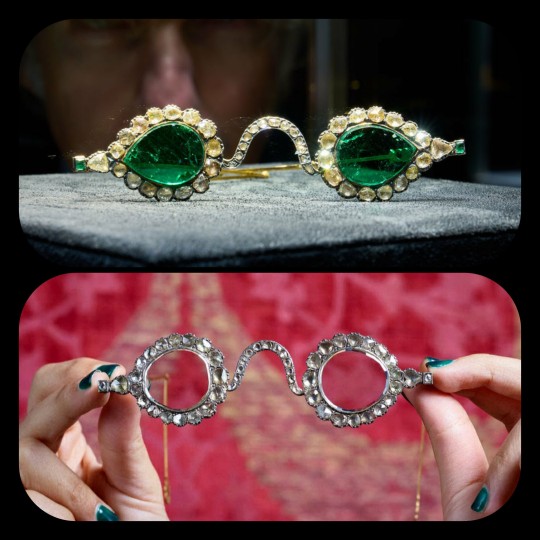

The Gate of Paradise and the Halo of Light were both kept in the collections of a wealthy Indian family until 1980, when they were sold to private collectors, and they were then put up for auction once again in 2021. They were most recently valued at about $2 million to $3.4 million per pair.
Sources & More Info:
Sotheby's: Mughal Spectacles
Architectural Digest of India: At Sotheby's auction, Mughal-era eyeglasses made of diamond and emerald create a stir
Only Natural Diamonds: Auspicious Sight & the Halqeh-e Nur Spectacles
The Royal Society Publishing: Cleaving the Halqeh-Ye Nur Diamonds
Gemological Institution of America: Two Antique Mughal Spectacles with Gemstone Lenses
Manuscript: From Satan's Crown to the Holy Grail: emeralds in myth, magic, and history
CNN: The $3.5 million Spectacles Said to Ward off Evil
BBC: Rare Mughal Era Spectacles to be Auctioned by Sotheby's
#history#archaeology#artifact#mughal#india#17th century#art#emerald#diamond#glasses#indian lore#islam#religion#mysticism#indian history#anthropology#spirituality#fashion
5K notes
·
View notes
Text

Today on the second advent and door no. 8 we have a lovely pair, La Grace and Shtandart
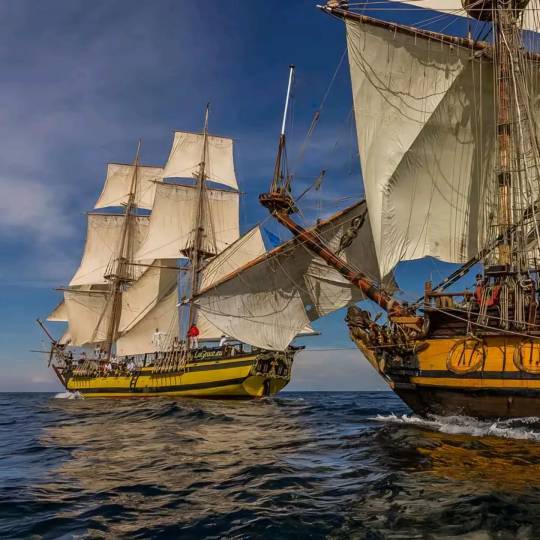

More about them here:
La Grace is a replica of a historic tall ship from the 18th century that will sail the seven seas like the original ship 300 years ago. The aim of the project is to give anyone interested the opportunity to sail a historic ship as part of the Navy's training programme and to share the proud traditions of sailing.
The brig was built between 2008 and 2010 by a group of volunteers from the Czech Republic and Slovakia in an Egyptian shipyard in Suez using traditional craft techniques. The brig was designed by its owners (Josef Dvorsky and Daniel Rosecky) according to technical drawings published in 1768 in the Architectura navalis mercatoria by the Swedish admiral Fredrik Henrik af Chapman.
According to available sources, the original La Grace was a ship owned by the first Czech naval captain Augustin Herrman, a famous navigator in Czech history. He sailed across the Atlantic in the service of the Dutch West India Company. After leaving the company, he commanded the small privateer ship La Grace. This relatively weak and vulnerable ship with six cannons brought large quantities of captured Spanish galleons to New Amsterdam every year.
The Shtandart is a replica of an 18th century frigate. The original was the first frigate built at the Olonez shipyard under Peter the Great and the first ship to be commissioned as a frigate for the Baltic Fleet. During the Great Northern War, Tsar Peter succeeded in conquering the area that would later become St Petersburg on the Neva. With the conquest of the fortress of Nöteborg in 1702, Lake Ladoga was removed from Swedish control and the Tsar hoped to gain access to Finland. The aim of these endeavours was to gain access to the Baltic Sea in order to establish a port city there for trade and naval purposes.
The frigate was built from 1702 at the Olonez shipyard on the Lodejner Feld on the River Swir near Lake Ladoga, where it was given its name in reference to the newly introduced Russian naval flag, a standard. Tsar Peter personally transferred the ship to the Baltic Sea in 1703. When seven Swedish ships of the line, five frigates and other small ships attacked the mouth of the Neva in June 1705, eight Russian frigates, presumably including the Schandart, lay behind a barrage of trees. In 1712 and 1713, she took part in troop landings in Swedish Finland near Vyborg. No further use is mentioned after this action. The ship was decommissioned as unserviceable in 1718. In 1723, the ship was scrapped in St. Petersburg.
According to another version, Tsar Peter had ordered the Schandart to be preserved as a reminder of the beginnings of the Russian fleet. Tsarina Catherine I ordered the condition of the Petrine ships to be examined in 1727. However, the Shtandart broke up while trying to take her out of the water.
As a result of the sanctions against Russia following the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022, Russian ships are denied access to European ports. However, following a request from the Président des Amis des Grands Voiliers association to the French Secretary of State, the Shtandart was granted permission to call at French and Spanish ports and has remained there ever since. There are plans to put her under the French flag, as her captain strongly distances themselves from Russia.
#naval history#tall ships#brig la grace#frigate shtandart#18th century#replicas#age of sail#advent calendar#day 8
108 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here's the full script for the most recent video, minus where I ad libbed:
Dr. Moumita Debnath, a 31 year old doctor trainee, was found dead on August 9th, 2024. After taking a break half-way through a 36 hour shift, her corpse was found on a blood stained mattress. Her body bore the wounds of torture, from the wounds to her eyes, her pelvis, genitals, arms and legs. As noted in The Publica’s report, “The post-mortem report also noted that over 150 mg of semen was recovered from the doctor’s body, indicating that up to 30 men could have been involved in the violation of Debath’s body. The normal volume of semen produced by a male upon ejaculation typically varies from 1.5 to 5.0 mg, according to the online medical encyclopedia MedlinePlus” (Biase). Her family was told that she died via suicide, though her wounds made it obvious that this was not the case; however, this claim allowed the principal of the school to avoid filing a police report. The attempts to hide the crime did not succeed, and have resulted in protests across India and the medical industry, both in response to the lack of protections for medical staff, and because of the attempt to hide the crime.
In the aftermath, searches for footage of Debnath’s gang rape have trended, as “According to Google Trends, queries such as “Moumita Debnath porn” and “Dr. Moumita Debnath video” have experienced surges across India, with “Moumita Debnath rap[e] video” experiencing a 110% increase in searches. As of the time of this writing, of all the queries associated with her name, “Moumita Debnath photo video” is the 5th most searched in India, while “Moumita Debath last video” is the 12th most searched overall” (Biase).
This isn’t the only horrific case of gang rape, torture, or extreme violence against women. In fact, back in 2023, Vidya Krishnan wrote an opinion piece published in the New York times on the topic titled, “In India’s Gang Rape Culture, All Women Are Victims”, where she writes:
It is the specific horror of gang rape that weighs most heavily on Indian women that I know. You may have heard of the many gruesome cases of women being gang-raped, disemboweled and left for dead. When an incident rises to national attention, the kettle of outrage boils over, and women sometimes stage protests, but it passes quickly. All Indian women are victims, each one traumatized, angry, betrayed, exhausted. Many of us think about gang rape more than we care to admit.
In 2011 a woman was raped every 20 minutes in India, according to government data. The pace quickened to about every 16 minutes by 2021, when more than 31,000 rapes were reported, a 20 percent increase from the previous year. In 2021, 2,200 gang rapes were reported to authorities.
But those grotesque numbers tell only part of the story: 77 percent of Indian women who have experienced physical or sexual violence never tell anyone, according to one study. Prosecutions are rare.
Indian men may face persecution because they are Muslims, Dalits (untouchables) or ethnic minorities or for daring to challenge the corrupt powers that be. Indian women suffer because they are women. Soldiers need to believe that war won’t kill them, that only bad luck will; Indian women need to believe the same about rape, to trust that we will come back to the barracks safe each night, to be able to function at all. (Krishnan)
Just from recent memory, I can recall several other horrifying cases.
In a rare case of justice, in May 2024, a pair of brothers were sentenced to death for the rape and murder of a 12 year old girl. To hide the crime, they then burned her alive in a coal furnace. (The Hindu Bureau)
In 2012, 22 year old Jyoti Singh was “beaten, gang-raped, and tortured in a private bus in which she was travelling with her male friend, Avnindra Pratap Pandey. There were six others in the bus, including the driver, all of whom raped the woman and beat her friend.” She later succumbed to her wombs, while her friend supposedly committed suicide. (Khan)
Many rape cases end with the woman dead. It is horrifying to me, from across the globe, to know that women live under constant threat of sexual assault, and while all assaults are horrific, the cases which break into the international news sphere from India are especially cruel and disturbing. It is the culmination of a deeply traditional and patriarchal society, wherein the devaluation of women is compounded with caste and religious issues, along with the rise of pornography. Porn is the instruction, and rape is the practice; though clearly, there was no need for instruction.
Famous cases include:
The Suryanelli rape case, where in 1996, a sixteen year old was lured with a marriage promise, kidnapped, and was raped by 37 men during her forty day captivity. Although initially 35 of 39 accused were found guilty, in 2005, all 35 convicted were acquitted of charges.
The Pararia mass rape, where in 1988, at least 14 women were gang raped by the police force, and had their homes looted after they protested against being removed to make way for a damn being built. “India Today reported Sinha's concluding statements were: "It cannot be ruled out that these ladies might speak falsehood to get a sum of Rs 1,000, which was a huge sum for them." (Bonner)
In many caste altercations, women are targeted because to rape a woman is not done just to her, but is meant to be an insult to the community and the community’s honor. In an environment where religious and social conflict occurs, women are especially vulnerable as targets of sexual violence.
However, what the internet has provided is an avenue to share the debasement and horror of gang rape with other men. It prolongs the suffering and harm to the victim and her family; but also serves as a warning to other women, and as an enticement to other men. Come, they say. Look at what we did. See how we were despicable and got away with it? You can too.
A 28 year old tourist and her husband were robbed, then man beaten, and the woman, raped by seven men in March of 2024. Since they have taken down the video detailing the event from their social media, I will not show that here, or go deeply into detail. However, in the reactions to the incident, one can note a pattern of behavior, not just from Indian men, but also women.
The BBC reported:
“The chief of India's National Commission for Women, Rekha Sharma, also sparked criticism after she responded to a post from a US journalist who wrote that while India was one of his favourite places, "the level of sexual aggression" he witnessed while living in the country was "unlike anywhere else I have ever been". He also gave a couple of examples of sexual assault faced by women he knew.
"Did you ever report the incident to police?" Ms Sharma wrote. "If not then you are totally an irresponsible person. Writing only on social media and defaming whole country is not good choice."” (Sebastian)
Victim blaming is constant, and serves as a deterrent from seeking help, reporting incidents, or enacting change. In the aftermath of the 2019 gang rape and murder of 27 year old Priyanka Reddy, Indian filmmaker Daniel Shravan ranted on social media that “The government should encourage and legalize rape without violence,” and, “Girls above 18 should be educated on rapes and not deny the sexual desires of men.” He also went on to say that, “Rapists are not finding a way to get their bodily sexual desires [met],” which is compelling them to kill.” (“After a Woman in India was Raped and Murdered, Her Name Trended on Porn Sites”). Because assault and violence against women is so common in India, it makes sense that victim blaming, from both sexes remains so strong, as “according to Inside Southern, the reason for victim blaming is: “People may blame a victim in order to remove themselves from an unpleasant event and therefore confirm their own invulnerability to the risk. Others may perceive the victim as different from themselves if they label or accuse the victim. People console themselves by saying, “Because I’m not like her, and I don’t do that, this would never happen to me.”” (Ram). In other words, it a pacifier, a way to manage the dread that comes with realizing the ubiquitousness and unpredictability of sexual assault. If there is something you can do to avoid being assaulted, then it must be her fault. And you must be safe, because you don’t make those choices.
That men make up a large contingent of the judges and lawmakers that in turn pass the laws which allow rapists to walk free iillustrates the universal truth that Anna Maria Mozzoni, a popular Italian feminist theorist, wrote about in 1895, “You will find that the priest who damns you is a man; that the legislator who oppresses you is a man, that the husband who reduces you to an object is a man; that the libertine [anarchist] who harasses you is a man; that the capitalist who enriches himself with your ill- paid work and the speculator who calmly pockets the price of your body, are men.”
It’s easy to forget when the violence is not happening in front of you, when you can excuse it, or look away, or claim that there are forces at play that you don’t understand. It’s easy to say that the problem is with a people or a religion-
But the truth is that woman hating is universal. A passing interest in anthropology will only show the manifestations of this hatred in creative ways throughout space and time.
Works Cited
“After a Woman in India was Raped and Murdered, Her Name Trended on Porn Sites.” Fight The New Drug, December 2019, https://fightthenewdrug.org/woman-in-india-raped-and-murdered-her-name-trended-on-porn/. Accessed 21 August 2024.
Biase, Natasha. “Name Of Female Doctor Who Was Gang Raped And Murdered In Indian Hospital Appears On Porn Sites As Men Seek Out Footage Of The Assault.” The Publica, 19 August 2024, https://www.thepublica.com/female-doctor-who-was-gang-raped-and-murdered-in-indian-hospital-appears-on-porn-sites-as-indian-men-search-for-footage-of-crime/. Accessed 21 August 2024.
Bonner, Arthur. “Pararia mass rape (1988).” Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pararia_mass_rape_(1988). Accessed 21 August 2024.
The Hindu Bureau. “Two get death for raping, burning alive minor girl in Bhilwara.” The Hindu, 20 May 2024, https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/rajasthan/two-sentenced-to-death-by-pocso-court-in-rajasthan-court-for-raping-burning-alive-minor-girl/article68195867.ece. Accessed 21 August 2024.
Khan, Aamir. “2012 Delhi gang rape and murder.” Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2012_Delhi_gang_rape_and_murder. Accessed 21 August 2024.
Krishnan, Vidya. “Opinion | In India's Gang Rape Culture, All Women Are Victims (Published 2023).” The New York Times, 2 June 2023, https://www.nytimes.com/2023/06/02/opinion/india-women-rape.html. Accessed 21 August 2024.
Ram, Anjali. “Never Ending Tales Of Victim Blaming And Shaming.” Feminism in India, 12 December 2022, https://feminisminindia.com/2022/12/12/never-ending-tales-of-victim-blaming-and-shaming/. Accessed 21 August 2024.
Sebastian, Meryl. “Outrage over Brazilian tourist's gang rape in India.” BBC, 3 March 2024, https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-india-68444993. Accessed 21 August 2024.
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
Researchers from Western and Brown University have made groundbreaking progress towards identifying the root cause and potential therapy for preeclampsia.
The pregnancy complication affects up to eight per cent of pregnancies globally and is the leading cause of maternal and fetal mortality due to premature delivery, complications with the placenta and lack of oxygen.
The research, led by Drs. Kun Ping Lu and Xiao Zhen Zhou at Western, and Drs. Surendra Sharma and Sukanta Jash at Brown, has identified a toxic protein, cis P-tau, in the blood and placenta of preeclampsia patients.
According to the study published in Nature Communications, cis P-tau is a central circulating driver of preeclampsia – a “troublemaker” that plays a major role in causing the deadly complication...
“The root cause of preeclampsia has (so far) remained unknown, and without a known cause there has been no cure. Preterm delivery is the only life-saving measure,” said Lu, professor of biochemistry and oncology at Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry...
“Our study identifies cis P-tau as a crucial culprit and biomarker for preeclampsia. It can be used for early diagnosis of the complication and is a crucial therapeutic target,” said Sharma...
Until now, cis P-tau was mainly associated with neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, traumatic brain injuries (TBI) and stroke. This association was discovered by Lu and Zhou in 2015 as a result of their decades of research on the role of tau protein in cancer and Alzheimer’s.
An antibody developed by Zhou in 2012 to target only the toxic protein while leaving its healthy counterpart unscathed is currently undergoing clinical trials in human patients suffering from TBI and Alzheimer’s Disease. The antibody has shown promising results in animal models and human cell cultures in treating the brain conditions.
The researchers were curious whether the same antibody could work as a potential treatment for preeclampsia. Upon testing the antibody in mouse models they found astonishing results.
“In this study, we found the cis P-tau antibody efficiently depleted the toxic protein in the blood and placenta, and corrected all features associated with preeclampsia in mice. Clinical features of preeclampsia, like elevated blood pressure, excessive protein in urine and fetal growth restriction, among others, were eliminated and pregnancy was normal,” said Sharma.
Sharma and his team at Brown have been working on developing an assay for early detection of preeclampsia and therapies to treat the condition. He believes the findings of this study have brought them closer to their goal...
“The results have far-reaching implications. This could revolutionize how we understand and treat a range of conditions, from pregnancy-related issues to brain disorders,” said Lu.
-via India Education Diary, September 22, 2023
#preeclampsia#maternal mortality#infant mortality#medical news#medical research#alzheimers#biology#pregnancy complications#good news#hope
322 notes
·
View notes
Text
HIS DAY IN GAY HISTORY
based on: The White Crane Institute's 'Gay Wisdom', Gay Birthdays, Gay For Today, Famous GLBT, glbt-Gay Encylopedia, Today in Gay History, Wikipedia, and more … January 1

I hope you are enjoying This Day in Gay History. It was started out as a reposting of White Crane's daily newsletters in early 2011 has gained a life of its own and grown out in many directions, in particular, gaining a international identity. The postings now come from many sources, some of them credited in the masthead, but also from tips and suggestions from members. As we move into a new year, you will find you have seen many of the postings before, but always check them out, because there will always be something new, especially as so many public figures are now coming out of the closet. Your Admin




1533 – Italy: Michelangelo writes a love letter to Tommaso de Cavalieri, devoting "the present and the time to come that remain to me."


Rare snapshot of Charles Kains Jackson
1857 – Charles Kains Jackson (d.1933) was an English poet closely associated with the Uranian school.
Beginning in 1888, in addition to a career as a lawyer, he served as editor for the periodical the Artist and Journal of Home Culture, which became something of an official periodical for the movement. In it, he praised such artists as Henry Scott Tuke (to whom he dedicated a sonnet) and Henry Oliver Walker. He also befriended such similar-minded contemporaries as Frederick William Rolfe, Lord Alfred Douglas and John Addington Symonds.The homosexual and pederastic aspects of the Artist declined after the replacement of Kains Jackson as an editor in 1894. The final issue edited by Kains Jackson included his essay, 'The New Chivalry', an argument for the moral and societal benefits of pederasty and erotic male friendship on the grounds of both Platonism and Social Darwinism. According to Kains Jackson, the New Chivalry would promote 'the youthful masculine ideal' over the Old Chivalry's emphasis on the feminine. Jackson's volumes of poetry include Finibus Cantat Amor (1922) and Lysis (1924).
Kains Jackson was a member of the Order of Chaeronea, a secret society for homosexuals founded in 1897 by George Ives, which was named after the location of the battle where the Sacred Band of Thebes was finally annihilated in 338 BC. Other members included Samuel Ellworth Cottam, Montague Summers, and John Gambril Nicholson.


1879 – E.M. Forster (d.1970) was an English novelist, short story writer, essayist and librettist. He is known best for his ironic and well-plotted novels examining class difference and hypocrisy in early 20th-century British society.
Forster was born into an Anglo-Irish and Welsh middle-class family in London. England. He attended the famous public school Tonbridge School in Kent as a day boy. The theatre at the school is named after him, and later studied at King's College, Cambridge, between 1897 and 1901.
After leaving university he travelled in continental Europe with his mother. He visited Egypt, Germany and India with the classicist Goldsworthy Lowes Dickinson in 1914. By that time, Forster had written all but one of his novels. In the First World War, as a conscientious objector, he volunteered for the International Red Cross, travelling to Alexandria, Egypt.
Why didn't EM Forster write much of anything in the second half of his life? According to a new biographer, Wendy Moffat, who has had access to Forster's private papers, what knocked him off track was losing his virginity in his late 30s.
He slept with a wounded soldier in Egypt, in 1917 - "losing R [respectability]" he called it in his private diary. After that, he set about making up for lost time. "I should have been a more famous writer if I had written or rather published more," he later explained, "but sex prevented the latter."
Back in England Forster divided his time between his mother in the Home Counties and gay friends and bisexual boys in his London flat. Homosexuality in Britain was aggressively persecuted then and Forster wisely centred his affairs on officers from Hammersmith police station.
One of them, Bob Buckingham, became the love of Forster's life. Bob was bisexual and soon married, however, he never abandoned Forster. As for writing novels that stopped with the development of his homosexual life.
Forster developed a long-term loving relationship with Bob Buckingham, and his wife, and included the couple in his circle, which also included the writer and arts editor of The Listener, J.R. Ackerley, the psychologist��W.J.H. Sprott, and, for a time, the composer Benjamin Britten. Other writers with whom Forster associated included the poet Siegfried Sassoon and the Belfast-based novelist Forrest Reid.
In the 1930s and 1940s Forster became a successful broadcaster on BBC Radio. He was a humanist, homosexual, and lifelong bachelor.
Forster had five novels published in his lifetime. Although Maurice appeared shortly after his death, it had been written nearly sixty years earlier. A seventh novel, Arctic Summer, was never finished. The earlier novels are Where Angels Fear to Tread (1905), The Longest Journey (1907), A Room with a View (1908), and Howards End (1910).
Forster achieved his greatest success with A Passage to India (1924). The novel takes as its subject the relationship between East and West, seen through the lens of India in the later days of the British Raj. Forster connects personal relationships with the politics of colonialism through the story of the Englishwoman Adela Quested, the Indian Dr. Aziz, and the question of what did or did not happen between them in the Marabar Caves.
Maurice (1971) - his one novel to deal head-on with homosexuality - was written some years previously, though it was published only after his death. His posthumously-published novel tells of the coming of age of an explicitly Gay male character.
Maurice is a homosexual love story which also returns to matters familiar from Forster's first three novels, such as the suburbs of London in the English home counties, the experience of attending Cambridge, and the wild landscape of Wiltshire. The novel was controversial, given that Forster's sexuality had not been previously known or widely acknowledged. Today's critics continue to argue over the extent to which Forster's sexuality, even his personal activities, influenced his writing.
Forster's two best-known works, A Passage to India and Howards End, explore the irreconcilability of class differences. A Room with a View also shows how questions of propriety and class can make connection difficult. The novel is his most widely read and accessible work, remaining popular long after its original publication. His posthumous novel Maurice explores the possibility of class reconciliation as one facet of a homosexual relationship.
Sexuality is another key theme in Forster's works, and it has been argued that a general shift from heterosexual love to homosexual love can be detected over the course of his writing career. The foreword to Maurice describes his struggle with his own homosexuality, while similar issues are explored in several volumes of homosexually-charged short stories. Forster's explicitly homosexual writings, the novel Maurice and the short-story collection The Life to Come, were published shortly after his death.
Forster died of a stroke in Coventry on 7 June 1970 at the age of 91. at the home of his policeman friend and his wife, the Buckinghams.


1895 – Although never elected to any office, J. Edgar Hoover (d.1972) wielded tremendous political power in the United States government for almost five decades, and through eight presidencies, as head of the Federal Bureau of Investigation. Under his leadership, the Bureau developed from a weak and ineffectual collection of political appointees into one of the most efficient police agencies in the world.
It also developed into an undercover secret police that frequently used illegal means to gather damaging information, not only on criminals and political dissidents, but also on political leaders as well. Although Hoover was always in the front lines of government attempts to harass homosexual liberation movements, rumors that he himself was gay followed him throughout his career.
Hoover went to work for the Justice Department in 1917 as a clerk, but moved up quickly by virtue of his efficiency and his vigorous action against Communists and radicals during the late 1910s and 1920s. He supervised the deportation of foreign-born radicals in the great strike wave of 1919.
In 1924, he was appointed head of the Bureau of Investigation of the Justice Department (renamed Federal Bureau of Investigation in 1935). Hoover immediately began to tighten up the slack Bureau. New agents were hired and promoted based on merit and strict performance reviews. He used his library experience to re-organize records and files, and he began amassing his famous "secret files," confidential information, often illegally obtained, which he kept to use against anyone who might threaten his power or tenure.
Hoover soon became both famous and feared for his zealous campaigns against such criminal and "subversive" groups as the Communist Party and the Ku Klux Klan. During the prohibition era, his "G-men" hunted down and caught many prominent gangsters, such as Al Capone and John Dillinger.
During the 1950s, he participated fully in the McCarthy witch hunts, zealously seeking out Communists and fellow-travelers.
Along with pursuing Communist sympathizers, Hoover also led a campaign of harassment directed at the new "homophile" groups such as the Mattachine Society, which sprang up to protest mistreatment of gay men and lesbians. F.B.I. agents took pictures and license plate numbers at demonstrations and infiltrated meetings and conferences of the fledgling homophile groups.
Many believe that Hoover took this anti-gay stance to cover his own homosexuality. Although he constantly (and violently) denied it, whispers about his sexuality followed Hoover throughout his career. For example, a 1943 internal F.B.I. memo reported claims that the director was homosexual.
Hoover's lifestyle fit many gay stereotypes: he was a sharp, dandified dresser, known for his white linen suits and silk handkerchiefs, who collected antiques and lived with his mother until her death when he was 42. He was never known to have even one date with a woman, yet he had several intimate relationships with men, notably a more than forty-year relationship with the handsome Clyde Tolson, his second-in-command at the F.B.I.
Hoover and Tolson rode to work together, ate lunch and dinner together most days, and took vacations together. Many observers described their relationship as marriage-like. Although some commentators believe that Hoover's rigid morality and strict religious beliefs would not have permitted him to have a physical relationship with a man, the rumors of his homosexuality were accelerated by the appearance, after their deaths, of photographs of Hoover and Tolson in drag, photographs that were allegedly Mafia blackmail pictures.
If Hoover and Tolson were homosexual, as seems more and more likely, their roles as persecutors of other homosexuals casts into bold relief the nightmare-like quality of the McCarthy era's war on homosexuality.
Hoover remained in charge of the F.B.I. until his death from a heart attack on May 2, 1972.


1927 – Maurice Béjart (d.2007) was a French born, Swiss choreographer who ran the Béjart Ballet Lausanne in Switzerland. He was the son of the French philosopher Gaston Berger.
Perhaps the preeminent descendant of Sergei Diaghilev and Serge Lifar, Maurice Béjart was a significant presence in late twentieth-century and early twenty-first century dance as an innovator with a radical vision. Central to his reinvigoration of classical ballet was his creation of palpably homoerotic dances that celebrate male beauty.
After studying with Léo Staats, Lubov Egorova, and Madama Rousanne (Sarkissian) in Paris, he performed with Mona Inglesby's International Ballet and the Royal Swedish Ballet and sealed his reputation as industrious and disciplined before creating dances for his own path-breaking companies.
Symphonie pour un homme seul (1955, with a score by Pierre Schaeffer and Pierre Henry), featuring the first electronic score to accompany ballet, established Béjart as an innovator with a radical vision.
After presenting an electrifying interpretation of The Rite of Spring (set to the classic Igor Stravinsky score) informed by myth, sexual heat, and stage flash in 1959 at the Théâtre Royale de la Monnaie in Brussels, he founded The Ballet of the Twentieth Century, a company that had a major influence on the European Dance Theatre movement.
Nijinsky: Clown of God (1971, set to a score combining music by Peter Ilich Tchaikovsky and Pierre Henry), a dreamlike meditation on Vaslav Nijinsky and his legacy, is only one prominent example of Béjart's personal identification and connection with his choreographic subjects.
Many times that connection, as in Nijinsky: Clown of God, was palpably homoerotic. In addition to reimagining Ballets Russes classics such as The Firebird (to the original Stravinsky score), Pétrouchka (to the Stravinsky score) and The Specter of the Rose (to a score of a piano piece by Carl Maria von Weber, orchestrated by Hector Berlioz) to spectacular effect, he also derived inspiration from such gay icons as Prometheus, Dionysus, Orpheus, and Saint Sebastian.
Collaborating closely with many extraordinarily handsome men (Argentine Jorge Donn and Italian Paolo Bortoluzzi among them), Béjart consistently created dances celebrating male beauty and eroticism, not the least of which was the all-male variant of his Boléro (1960, to the throbbing score by Maurice Ravel).
Audiences and critics were either enthralled or enraged by later offerings such as the celebratory Ballet for Life (1997, set to a score combining classical Mozart with pop-rock Queen), in response to the AIDS-related deaths of his friends Jorge Donn and Freddie Mercury of the rock group Queen; and Bolero for Gianni (1999, set to his all-time-favorite Ravel score), a tribute to the murdered Gianni Versace, who had designed the eye-popping costumes for that 1997 dance.
Although beset by kidney problems and other illnesses in his final years, Béjart continued working until the very end of his life. He died on November 22, 2007.


1944 – Eloy de la Iglesia (d.2006) was a Spanish screenwriter and film director.
De la Iglesia was an outspoken gay socialist filmmaker who is relatively unknown outside Spain despite a prolific and successful career in his native country. He is best remembered for having portrayed urban marginality and the world of drugs and juvenile delinquency in the early 1980s. Many of his films also deal with the theme of homosexuality.
Born in Zarauz, Guipúzcoa into a wealthy Basque family, he grew up in Madrid. He attended courses at the prestigious Parisian Institut des hautes études cinématographiques, but he could not enter Spain’s national Film School because he wasn't yet 21, the minimum age required for admission. Instead, he began to study philosophy and literature at the Complutense University of Madrid, but on his third year he abandoned it to direct children’s theater. By age twenty he had already written and directed many works for television sharpening his narrative skills. He established himself as a writer of children's television programs for Radiotelevisíon Española in Barcelona.
De la Iglesia made his debut as film director when he was only twenty-two years old with Fantasia 3 (Fantasy 3) (1966), adapting three children’s stories: The Maid of the Sea, The three hairs from the devil and The Wizard of Oz. While doing mandatory military service, he wrote the script of his second film, Algo Amargo en la Boca (Something Bitter Tasting) (1968). Algo Amargo en la boca, a sordid melodrama, and de la Iglesia’s next film, Cuadrilatero (Boxing Ring) (1969), a boxing story, faced problems with the Francoist censors and failed at the box office. His films did not attract widespread notice until his fourth effort, the critically acclaimed thriller El Techo de Cristal (The Glass Ceiling) (1970).
The dismantling of the Francoist censorship allowed Eloy de la Iglesia to increase sexually charged tones in his works. This approach became apparent in his films: Juego de amor prohibido (Games of Forbbiden Love) (1975) and La otra alcoba (The other bedroom) (1976). In the late 1970s Eloy de la Iglesia, associated with journalist and screen writer Gonzalo Goicoechea, tackled former taboo subjects in Spanish Cinema. Los placeres ocultos (Hidden Pleasures ) (1977) focused on homosexuality. El diputado (Confessions of a Congressman) (1979), follows the story of a politician who is blackmailed due to his secret homosexuality and El sacerdote (The Priest ), also released in 1979, deals with a conservative catholic priest whose sexual obsessions leads him to self-mutilation.
Like many of the young protagonists of his films, Eloy de la iglesia became addicted to drugs such as heroin and he stopped making films for fifteen years. Claiming that his addiction to cinema was stronger than his drug problems, de la Iglesia eventually kicked his habit and resumed his career making Los novios bulgaros (The Bulgarian Lovers) (2003), a film based on the novel of the same title written by Eduardo Mendicutti.
Stricken with kidney cancer, he died on March 24, 2006, age sixty two, after surgery to remove a malignant tumor.


1959 – Fidel Castro seized power in Cuba after leading a revolution that drove out dictator Fulgencio Batista. Castro then established a Communist dictatorship. Although homosexuality was illegal under the Batista government the laws were largely ignored in fun loving Cuba. Since Castro, tens of thousands of gays have been rounded up and imprisoned.


1967 – The Los Angeles Police Department raid the New Year’s Eve parties at two gay bars, the Black Cat Tavern and New Faces. Several patrons were injured and a bartender was hospitalized with a fractured skull. Several hundred people spontaneously demonstrate on Sunset Boulevard and picket outside the Black Cat. The raids prompted a series of protests that began on 5 January 1967, organized by P.R.I.D.E. (Personal Rights in Defense and Education). It’s the first use of the term "Pride" that came to be associated with LGBT rights and fuels the formation of gay rights groups in California, well before the Stonewall Riot.
The popular notion that the Stonewall Riots marked the very first time that LGBT folks "fought back instead of passively enduring humiliating treatment,” is false. Other critical moments in LGBT History that pre-date Stonewall include:
New Year's Ball Raid in San Francisco (1965)
Gene Compton’s Cafeteria Riot (1966)
Cooper Do-Nuts Riot (1959)


1968 – Joey Stefano (d.1994) was an American pornographic actor who appeared in gay adult films. Born Nicholas Anthony Iacona, Jr., Stefano grew up in the Philadelphia area (Chester, Pennsylvania). His father died when he was 15. After several years of prostitution and hard-core drug use in New York City, Stefano moved to Los Angeles and quickly became a star in gay pornography. In addition to his good looks, his persona as a "hungry bottom" (sexually submissive but verbally demanding) contributed to his popularity.
His image and success caught the attention of Madonna, who used him as a model in her 1992 book Sex.
During his lifetime, he was the subject of rumors (some of them spread by himself) regarding his relationships with prominent entertainment industry figures who were known to be gay. At a May 1990 dinner and interview with Jess Cagle (Entertainment Weekly) and Rick X (Manhattan Cable TV's The Closet Case Show), Stefano discussed an alleged series of "dates" with David Geffen, who at one point implored Stefano to quit using drugs. After the videotaped interview appeared on Rick X's show, OutWeek Magazine "outed" Geffen, who went on to announce his homosexuality at an AIDS fundraiser.
He was HIV positive. According to a subsequent biography Stefano died of speedball overdose (cocaine, morphine, heroin, and ketamine) at age 26 in the shower of a motel on Sunset Boulevard in Hollywood, California. His body was taken back to Pennsylvania where he was buried next to his father.
Stefano's life is chronicled in the book, Wonder Bread and Ecstasy: The Life and Death of Joey Stefano by Charles Isherwood. His life is also the subject of a one-man-play, Homme Fatale: The Fast Life and Slow Death of Joey Stefano, by Australian playwright Barry Lowe.


1976 – (Daniel L.) Dan Kloeffler is an American television journalist. Since 2010, he is an anchor of ABC News Now, a cable-news channel of the ABC broadcasting network.
He worked at WSTM-TV - an NBC-affiliated television station in Syracuse, New York - prior to joining MSNBC, a cable-news channel. While at MSNBC, he anchored overnight MSNBC Now news updates as well as MSNBC's First Look and broadcast network NBC's Early Today, both early-morning news programs; Kloeffler left MSNBC in 2009. In 2010, he became a freelance anchor and correspondent for ABC News, where he anchors on its ABC News Now channel.In response to the news that actor Zachary Quinto had come out as gay, Kloeffler publicly came out on the air in October 2011.
In a statement on the ABC News website, he wrote that a series of suicides by gay youth also led him to hope his being publicly out would help encourage young gay people struggling to accept themselves.


2008 – Queen Elizabeth II makes actor Ian Mckellen a Companion of Honor, one of only 65.


21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just in case. Some might enjoy. Had to organize some notes.
These are just some of the newer texts that had been promoted in the past few years at the online home of the American Association of Geographers. [At: aag dot org/new-books-for-geographers/]
Tried to narrow down selections to focus on (1) Indigenous, Black, Latin American, oceanic/archipelagic geographies; (2) imaginaries and environmental perception; (3) and mobility, borders, carceral/abolition geography.
These texts feature concepts/subjects like: Indigeneity and "geographies of time" in the Ecuadorian Andes. "Migration and music in the construction of precolonial AfroAsia." The "practice of collective escape" and "reimagining geographies of order." The "making and unmaking of French India." The "literary geography" of the rubber boom in Amazonia. "Coercive geographies" and mass imprisonment. "Anti-fatness as anti-Blackness." The "(un)governable city" of colonial Delhi.
---
New stuff, early 2024:
A Caribbean Poetics of Spirit (Hannah Regis, University of the West Indies Press, 2024)
Constructing Worlds Otherwise: Societies in Movement and Anticolonial Paths in Latin America (Raúl Zibechi and translator George Ygarza Quispe, AK Press, 2024)
Fluid Geographies: Water, Science, and Settler Colonialism in New Mexico (K. Maria D. Lane, University of Chicago Press, 2024)
Hydrofeminist Thinking With Oceans: Political and Scholarly Possibilities (Tarara Shefer, Vivienne Bozalek, and Nike Romano, Routledge, 2024)
Making the Literary-Geographical World of Sherlock Holmes: The Game Is Afoot (David McLaughlin, University of Chicago Press, 2025)
Mapping Middle-earth: Environmental and Political Narratives in J. R. R. Tolkien’s Cartographies (Anahit Behrooz, Bloomsbury Publishing, 2024)
Midlife Geographies: Changing Lifecourses across Generations, Spaces and Time (Aija Lulle, Bristol University Press, 2024)
Society Despite the State: Reimagining Geographies of Order (Anthony Ince and Geronimo Barrera de la Torre, Pluto Press, 2024)
---
New stuff, 2023:
The Black Geographic: Praxis, Resistance, Futurity (Camilla Hawthorne and Jovan Scott Lewis, Duke University Press, 2023)
Activist Feminist Geographies (Edited by Kate Boyer, Latoya Eaves and Jennifer Fluri, Bristol University Press, 2023)
The Silences of Dispossession: Agrarian Change and Indigenous Politics in Argentina (Mercedes Biocca, Pluto Press, 2023)
The Sovereign Trickster: Death and Laughter in the Age of Dueterte (Vicente L. Rafael, Duke University Press, 2022)
Ottoman Passports: Security and Geographic Mobility, 1876-1908 (İlkay Yılmaz, Syracuse University Press, 2023)
The Practice of Collective Escape (Helen Traill, Bristol University Press, 2023)
Maps of Sorrow: Migration and Music in the Construction of Precolonial AfroAsia (Sumangala Damodaran and Ari Sitas, Columbia University Press, 2023)
---
New stuff, late 2022:
B.H. Roberts, Moral Geography, and the Making of a Modern Racist (Clyde R. Forsberg, Jr.and Phillip Gordon Mackintosh, Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2022)
Environing Empire: Nature, Infrastructure and the Making of German Southwest Africa (Martin Kalb, Berghahn Books, 2022)
Sentient Ecologies: Xenophobic Imaginaries of Landscape (Edited by Alexandra Coțofană and Hikmet Kuran, Berghahn Books 2022)
Colonial Geography: Race and Space in German East Africa, 1884–1905 (Matthew Unangst, University of Toronto Press, 2022)
The Geographies of African American Short Fiction (Kenton Rambsy, University of Mississippi Press, 2022)
Knowing Manchuria: Environments, the Senses, and Natural Knowledge on an Asian Borderland (Ruth Rogaski, University of Chicago Press, 2022)
Punishing Places: The Geography of Mass Imprisonment (Jessica T. Simes, University of California Press, 2021)
---
New stuff, early 2022:
Belly of the Beast: The Politics of Anti-fatness as Anti-Blackness (Da’Shaun Harrison, 2021)
Coercive Geographies: Historicizing Mobility, Labor and Confinement (Edited by Johan Heinsen, Martin Bak Jørgensen, and Martin Ottovay Jørgensen, Haymarket Books, 2021)
Confederate Exodus: Social and Environmental Forces in the Migration of U.S. Southerners to Brazil (Alan Marcus, University of Nebraska Press, 2021)
Decolonial Feminisms, Power and Place (Palgrave, 2021)
Krakow: An Ecobiography (Edited by Adam Izdebski & Rafał Szmytka, University of Pittsburgh Press, 2021)
Open Hand, Closed Fist: Practices of Undocumented Organizing in a Hostile State (Kathryn Abrams, University of California Press, 2022)
Unsettling Utopia: The Making and Unmaking of French India (Jessica Namakkal, 2021)
---
New stuff, 2020 and 2021:
Mapping the Amazon: Literary Geography after the Rubber Boom (Amanda Smith, Liverpool University Press, 2021)
Geopolitics, Culture, and the Scientific Imaginary in Latin America (Edited by María del Pilar Blanco and Joanna Page, 2020)
Reconstructing public housing: Liverpool’s hidden history of collective alternatives (Matt Thompson, University of Liverpool Press, 2020)
The (Un)governable City: Productive Failure in the Making of Colonial Delhi, 1858–1911 (Raghav Kishore, 2020)
Multispecies Households in the Saian Mountains: Ecology at the Russia-Mongolia Border (Edited by Alex Oehler and Anna Varfolomeeva, 2020)
Urban Mountain Beings: History, Indigeneity, and Geographies of Time in Quito, Ecuador (Kathleen S. Fine-Dare, 2019)
City of Refuge: Slavery and Petit Marronage in the Great Dismal Swamp, 1763-1856 (Marcus P. Nevius, University of Georgia Press, 2020)
#abolition#ecology#multispecies#landscape#tidalectics#indigenous#ecologies#archipelagic thinking#opacity and fugitivity#geographic imaginaries#caribbean#carceral geography#intimacies of four continents#reading list#reading recommendations#book recommendations#my writing i guess#indigenous pedagogies#black methodologies
71 notes
·
View notes
Note
How many love interest did Alexander have in all of his life? I just recently found out he had an affair with a prostitute named Camaspe and apparently she was the one who was the first to have a physical relationship with him although not for long.
Love your work! 💕
Alexander’s Reported Lovers
Just an FYI … Kampaspe (Campaspe in Latin, also Pancaste) is a character in the second volume of Dancing with the Lion (Rise), as I wanted a second female voice and also a slave’s perspective. Even better that she was born to privilege, then lost it. She was reportedly a Thessalian hetaira from Larissa, which was handy as the Argeads had a long history of ties to the city of Larissa. I wrote about her before in a post from the blog tour the publisher had me do when the books first came out. You can read it HERE.
That said, she’s probably a Roman-era invention, mentioned only by late sources (Lucian, Aelian, and Pliny) all with one (repeated) story: Alexander as Super-patron. Reputedly, he gave her to his favored painter Apelles when, commissioned to do a nude, Apelles fell in love with her. Alexander kept the painting, Apelles got the girl. You bet I’ll have some fun with that. Kampaspe will remain a major character throughout the series…but not as Alexander’s mistress.

When trying to figure out how many sexual partners Alexander had, we must ask which were invented—or denied. Remember: ancient history wasn’t like modern (academic) history. It was essentially creative non-fiction. It inserted speeches, dialogue, even people and events to liven things up and/or to make a moral point. Or it obscured people and events, if that worked better.
Modern readers of ancient sources must always ask WHO wrote this, WHEN was it written, and what POINT did the author intend? Also, especially with anecdotes, look at the wider context. People are especially prone to take anecdotes at face value and treat them as isolated little tales. Yet CONTEXT IS KING.
A lot of our information about Alexander’s love life comes from Plutarch, either in his Life of Alexander or his collection of essays now called the Moralia. Another source is Curtius’s History of Alexander. And finally, Athenaeus’s Diepnosophistai or The Supper Party (really, The Learned Banqueters). All wrote during the Roman empire and had tropes and messages to get across.
Of the WOMEN associated with Alexander, I’m going to divide them into the historical and the probably fictional, or at least their relationship with Alexander was fictional.
Of the certain, we can count one mistress, three wives, and one probable secret/erased liaison.
Barsine is his first attested mistress for whom we have ample references across multiple sources. Supposedly, she bore Alexander a son (Herakles). Herakles certainly existed, but whether he was Alexander’s is less clear to me. As the half-Persian, half-Greek daughter of a significant satrap, she had no little influence. Monica D’Agostini has a great article on Alexander’s women, btw, in a forthcoming collection I edited for Colloquia Antiqua, called Macedon and Its Influences, and spends some time on Barsine. So look for that, probably in 2025, as we JUST (Friday) submitted the last of the proof corrections and index. Whoo! Anyway, Monica examines all Alexander’s (historical) women in—you guessed it!—their proper context.
Alexander also married three times: Roxane, daughter of the warlord Oxyartes of Sogdiana, in early 327. He married again in mid-324 in Susa, both Statiera (the younger), daughter of Darius, and Parysatis, youngest daughter of the king before Darius, Artaxerxes III Ochus. Yes, both at once, making ties to the older and the newer Achaemenid royal lines.
Out of all these, he had only one living son, Alexander IV (by Roxane)—although he got his women pregnant four times. If we can trust a late source (Metz Epitome), and I think we can for this, Roxane had a miscarriage while in India. Also, Statiera the younger was reputedly pregnant when Roxane, with Perdikkas’s help, killed her just a few days (or hours!) after Alexander died.
That’s 3 …who had baby #4?
Statiera the Elder, Darius’s wife. Netflix’s proposal of a liaison between them was not spun out of thin air. Plutarch—the same guy who tells us ATG never even looked at her—also tells us she died in childbirth just a week or three before the battle of Gaugamela, Oct. 1, 331. Keep in mind, Alexander had captured her right after Issos, Nov. 5, 333. Um … that kid wasn’t Darius’s. And if you think ANYbody would have been allowed to have an affair with such a high-ranking captive as the Great-King’s chief wife, I have some swampland in Florida to sell you. More on it HERE.
Now, for the probably fictional….
Kampaspe, I explained above.
Kallixena was supposedly hired by Philip and Olympias (jointly!) to initiate Alexander into sex, because he didn’t seem interested in women. (Yes, this little titbit is also in Rise.) Athenaeus reports the story as a digression on Alexander’s drinking, and how too much wine led to his lack of sexual interest. But within the anecdote, the reported reason for his parents’ hiring Kallixena was because mommy and daddy feared Alexander was “womanish” (gunnis).
Thaïs was linked to him by Athenaeus, almost certainly based on her supposed participation in the burning of Persepolis…which didn’t happen (or not as related; archaeology tosses cold water on it). Thaïs was Ptolemy’s mistress, and the mother of some of his children.
Athenaeus also mentions a couple unnamed interests, but all illustrate the same point: Alexander is too noble to steal somebody else’s love. Two are back-to-back: the flute-girl of a certain Theodoros, Proteas’ brother, and the lyre player of Antipatrides. The last is a boy, the eromenos of a certain Kalchis, a story related apart from the women, but with the same point.
Even more clearly fictional are his supposed encounters with the Amazon Queen Thalestris and Queen Kleophis of the Massaga (in Pakistan). Reportedly, as Onisikritos was reading from his history of Alexander at the court of King Lysimachos (who’d been a close friend, remember), Lysimachos burst out laughing when Onisikritos got to the Amazon story, and asked, “Where was I when this happened?”
Now, when it comes to his MEN/BOYS, the ice is thinner as no names are definitively given except Bagoas (in a couple sources, chiefly Curtius and Athenaeus). We also have a few generic references to pretty boys, as with Kalchis’s boyfriend mentioned above, and some slave boys offered by a certain Philoxenos, who he turns down, a story told by both Plutarch and Athenaeus.
Curtius alone suggests two more, but at least one is meant to show Alexander’s descent into Oriental Corruption(tm), so it’s possible Curtius made them up. At the very least, he used them for his own narrative purposes. Sabine Müller has a great article on this, albeit in German. Still, if you can read German: “Alexander, Dareios und Hephaistion. Fallhöhen bei Curtius Rufus.” In H. Wulfram, ed., Der Römische Alexanderhistoriker Curtius Rufus: Erzähltechnik, Rhetorik, Figurenpsychologie und Rezeption. Vienna: Austrian Academy of Sciences Press, 2016, 13-48.
Romans had a certain dis-ease with “Greek Love,” especially when it involved two freeborn men. Fucking slaves was fine; they’re just slaves. Citizen men with citizen boys…that’s trickier.
Curtius labels two youths “favorites,” a phrasing that implies a sexual affair. One is mentioned early in the campaign (Egypt) when Alexander is still “good”; the other after Alexander begins his slide into Persian Debauchery. These are Hektor, Parmenion’s son (good), and Euxinippos, described as being as pretty as Hephaistion, but not as “manly” (bad). Curtius employs Bagoas similarly, even claims he influenced imperial policy for his own dastardly goals. Gasp!
Yes, of course I’m being sarcastic, but readers need to understand the motifs that Curtius is employing, and what they really mean. Not what 21st century people assume they mean, or romantically want them to mean. (See my "Did Bagoas Exist?" post.)
What about Hephaistion? I’ve discussed him elsewhere in an article, but I’ll just remind folks that it’s nowhere made explicit until late sources, in large part because, by the time we meet Alexander and Hephaistion in the histories, they were adults, and any affair between them would be assumed to have occurred in the past, when they were youths. (See my “It’s Complicated” and a reply to them maybe being “DudeBros.”)
This is why we hear about Alexander’s interest in youths, not adult men. It would be WEIRD to the ancient mind (= Very Very Bad) if he liked adult men. In fact, by comparing Hephaistion to Euxinippos, Curtius slyly insinuates that maybe he and Alexander were still…you know (wink, wink). That’s meant to be a slam against Alexander (and Hephaistion)! Therefore, we cannot take it, in itself, as proof of anything. Alexander’s emotional attachment to Hephaistion, however, is not doubted by any ancient source.
So, all those people are attached to Alexander in our sources, but over half may not be real, or at least, may not have had a sexual relationship with him. There may be (probably are) some that simply didn’t make it into the surviving sources.
Yet I’ve mentioned before that we just don’t find sexual misconduct as one of Alexander’s named faults. Even Curtius and Justin must dig for it/make up shit, such as claiming Alexander actually used Darius’s whole harem of concubines or held a drunken revel through Karia after escaping the Gedrosian Desert. (Blue Dionysos and drag queens on the Seine at the Paris Olympics got nothing on his Dionysian komos!)
Drink, anger, hubris…he sure as hell ticked all those boxes. But not sex. In fact, a number of sources imply he just wasn’t that randy, despite his “choleric” temperament. Some of the authors credit too much drink (bad), others, his supreme self-control (good). He’s more often an example of sexual continence—as in the stories from Athenaeus related above. He also didn’t rape his captives, etc., etc.
Make of that what you like, but I find it intriguing.
#asks#Alexander the Great#Lovers of Alexander the Great#Alexander's Lovers#Hephaistion#Hephaestion#Bagoas#Barsine#Kampaspe#Kallixena#Statiera#Parysatis#Roxane#Thais#sexuality of Alexander the Great#Alexander the Great and sex#Alexander the Great and women#Alexander the Great and men#Classics#ancient Greek sexuality#ancient Greece#ancient Macedonia#Alexander x Hephaistion#Alexander x Hephaestion#tagamamnon
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
By: Himani Chandna
In India, experts said symptoms attributed to long Covid such as fatigue and concentration issues may overlap with common paediatric conditions like stress, anaemia, or viral syndromes, leading to underreporting
Children experience weakened immunity and bacterial infections after suffering from long Covid-19 syndrome, a study published in the medical journal Nature has revealed.
Persistent fatigue was the most common symptom in children with long Covid syndrome, while the majority of children often complained about anxiety.
The study conducted in Budapest, Hungary, investigated children affected by long Covid. The researchers found significant differences in their immune function, which they believe were caused by the Covid-19 infection.
“Neutrophil dysfunction in children with Long Covid syndrome (LCS) may be part of the disease pathogenesis or a predisposing factor," concluded the authors of the study published on November 27.
The researchers focused on a type of white blood cell called neutrophils, which plays a crucial role in combating infections, particularly bacterial ones. They discovered that children with long Covid had neutrophils that were functionally impaired.
“For instance, their ability to attack and swallow harmful bacteria such as Staphylococcus was impaired. This might correlate with the rise of multiple bacterial infections that were reported in Western nations among children after the onset of the pandemic," explained Rajeev Jayadevan, chairman, research cell, at the Indian Medical Association’s Kerala wing.
“After an expected drop following lockdowns, Group A streptococcal infection among younger children had surged in 2022, some of which turned severe. Whether this immune dysfunction accompanying long Covid was responsible for these additional infections is unclear."
What does the study say? To enhance the accuracy, the authors included both healthy children and those who had recovered without complications from Covid-19. Among the children with long Covid, seven of 10 experienced fatigue, while half had a loss of interest and difficulty concentrating. There was no difference in long Covid symptoms between vaccinated and unvaccinated children.
Long Covid Syndrome (LCS) children experienced significantly more symptoms, impairing their quality of life and functioning compared to CG+ group or convalescent children who have recovered from something like a febrile illness.
“Neutrophilic granulocyte dysfunction was found in LCS children, with decreased superoxide-producing activity and phagocytosis compared to CG+. The number of children with LCS complaints correlated significantly with altered neutrophil effector functions," said the study titled ‘Long COVID syndrome in children: neutrophilic granulocyte dysfunction and its correlation with disease severity’.
Neutrophilic granulocyte dysfunction is a problem with a specific type of white blood cells called neutrophils, which are important for fighting infections. These neutrophils are called granulocytes because they contain granules that help them destroy pathogens.
The neutrophils in children with LCS produce less of a molecule called superoxide, which is a chemical used by neutrophils to kill bacteria and other pathogens. Hence, it means that these neutrophils are less effective at destroying and cracking down on harmful invaders like bacteria.
When compared to the CG+ control group who did not have long Covid, their neutrophils did not show these problems.
The number of children with LCS complaints correlated significantly with altered neutrophil effector functions, which means that the severity or presence of symptoms in children with long Covid was closely related to the dysfunction of these neutrophil activities (superoxide production and phagocytosis). In other words, the more severe the symptoms of long Covid, the more likely there was an issue with the neutrophils’ ability to perform these critical immune functions.
However, in India, experts said they are not encountering many such cases in their clinical practice.
“We are not encountering such cases in large numbers. It likely reflects the low prevalence or a shift in disease dynamics," said Dr Maninder Dhaliwal, an expert in paediatric pulmonology at NCR-based Amrita Hospital.
“Another side to the story is that symptoms attributed to long Covid (e.g. fatigue, concentration issues) may overlap with common paediatric conditions like stress, anaemia, or viral syndromes, leading to maybe underreporting."
However, doctors pointed out that this study doesn’t translate to actionable diagnostic tools, therapeutic strategies, or preventive measures, but seems currently to serve more as academic knowledge.
“However, for children presenting with lingering fatigue, brain fog, or other long Covid symptoms, this knowledge may prompt closer monitoring or referral to the right specialists (e.g., immunology, neurology)," Dhaliwal added.
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#pandemic#wear a respirator#covid#covid 19#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2#long covid#covid in children
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
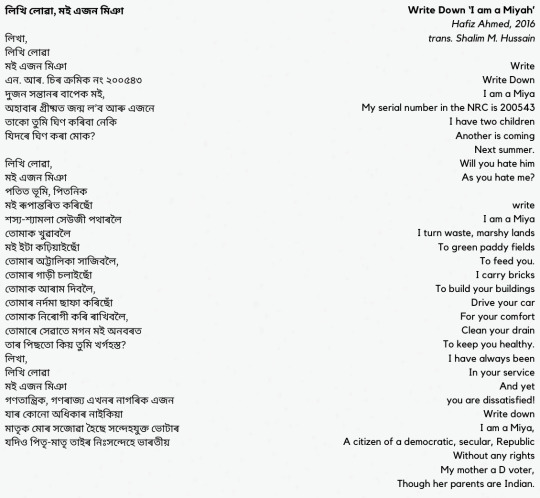

লিখি লোৱা, মই এজন মিঞা ("Write Down 'I am a Miyah'", 2016) by Hafiz Ahmed, translated from Assamese to English by Shalim M. Hussain, began a movement of resistance poetry among Assamese Muslims of Bengali descent, referred to as Miya Poetry after a slur used to describe this community. From Abdul Kalam Azad, for Indian Express ("Write...I am a Miya", 2019):
This poem went viral and other young poets started responding to him through poems. The young poets also started reclaiming “Miya”, a slur used against us, as our identity with pride. This chain of Facebook posts continued for days, reiterating the violence, suffering and humiliation expressed by our community. As time passed, more poets wrote in various languages and dialects, including many Miya dialects. The nomenclature ‘Miya Poetry’ got generated organically but the poets and their associates have been inspired by the Negritude and Black Arts movements, and queer, feminist and Dalit literary movements, where the oppressed have reclaimed the identity which was used to dehumanise them. The trend transcended our community. Poets from the mainstream Assamese community also wrote several poems in solidarity with the Miya poets while some regretted not being poets. Gradually, this became a full-fledged poetry movement and got recognised by other poets, critics and commentators. The quality and soul of these poems are so universal that they started finding prominence on reputed platforms. For the first time in the history of our community, we had started telling our own stories and reclaiming the Miya identity to fight against our harassers who were dehumanising us with the same word. They accused us of portraying the whole Assamese society as xenophobic. The fact is we have just analysed our conditions. Forget generalising the Assamese society as ‘xenophobic’, no Miya poet has ever used the term ‘xenophobic’ nor any of its variants. The guilt complex of our accusers is so profound that they don’t have the patience to examine why we wrote the poems.
Amrita Singh, writing for The Caravan ("Assam Against Itself", 2019), detailed the political backlash against Miya Poetry, in particular the above poem.
On 10 July this year, Pranabjit Doloi, an Assam-based journalist, filed a complaint at Guwahati’s Panbazar police station accusing ten people of indulging in criminal activities “to defame the Assamese people as Xenophobic in the world.” Doloi claimed that the ten people were trying to hinder the ongoing updation of the National Register of Citizens, a list of Assam’s Indian citizens that is due to be published on 31 August. The premise of Doloi’s complaint was a widely-circulated poem called, “Write down I am Miya,” by Hafiz Ahmed, a school teacher and social activist. “Write. Write down I am a Miya/ A citizen of democratic secular republic without any rights,” Ahmed wrote. The police registered a first information report against Doloi’s complaint, booking all ten persons for promoting enmity between groups, among other offences. [...] At the press conference, Mander emphasised that people in Assam are in distress because of the NRC’s arbitrary and rigid procedures. “One spelling mistake when you are writing a Bengali name in English … that is enough for you to be in a detention center, declared a foreigner,” Mander said. “If you are not allowing this lament to come out in the form of poetry, then where is this republic of India going?”
Ahmed's poem is influenced in structure by "Identity Card", a 1964 poem by by Palestinian poet Mahmoud Darwish which uses the symbolic figure of the Palestinian working man to confront Israeli occupiers. Darwish's identity card, a symbol of Israeli subjugation transformed into a cry of Palestinian national identity, is reshaped by Ahmed into the National Register of Citizens for Assam and the accompanying fear of statelessness and disenfranchisement for the Miya people.
This solidarity between writers from oppressed groups is, of course, not one that ends with Darwish and Ahmed, nor with the Black, queer, feminist, and Dalit influences of Miya Poetry. As long as there is oppression, there will be companionship and recognition reflected in art and activism. On December 13, 2023, Black Agenda Report reprinted Refaat Alareer's "If I Must Die", acknowledging the connection between Alareer's poem and "If We Must Die" by Claude McKay, written in 1919 in response to the Red Summer white supremacist riots. In 2000, Haitian community activist Dahoud Andre translated "If We Must Die" into Kreyòl, and the Black Agenda Report editorial honors Alareer in a similar way, reprinting "If I Must Die" with an accompanying Kreyòl translation. (POEM: If I Must Die, Refaat Alareer, 2023.)
Transcripts under the cut.




[Hafiz Ahmed Transcripts (Assamese and English):
লিখি লোৱা, মই এজন মিঞা
লিখা, লিখি লোৱা মই এজন মিঞা এন. আৰ. চিৰ ক্রমিক নং ২০০৫৪৩ দুজন সন্তানৰ বাপেক মই, অহাবাৰ গ্ৰীষ্মত জন্ম ল’ব আৰু এজনে তাকো তুমি ঘিণ কৰিবা নেকি যিদৰে ঘিণ কৰা মোক?
লিখি লোৱা, মই এজন মিঞা পতিত ভূমি, পিতনিক মই ৰূপান্তৰিত কৰিছোঁ শস্য-শ্যামলা সেউজী পথাৰলৈ তোমাক খুৱাবলৈ মই ইটা কঢ়িয়াইছোঁ তোমাৰ অট্টালিকা সাজিবলৈ, তোমাৰ গাড়ী চলাইছোঁ তোমাক আৰাম দিবলৈ, তোমাৰ নৰ্দমা ছাফা কৰিছোঁ তোমাক নিৰোগী কৰি ৰাখিবলৈ, তোমাৰে সেৱাতে মগন মই অনবৰত তাৰ পিছতো কিয় তুমি খৰ্গহস্ত? লিখা, লিখি লোৱা মই এজন মিঞা গণতান্ত্ৰিক, গণৰাজ্য এখনৰ নাগৰিক এজন যাৰ কোনো অধিকাৰ নাইকিয়া মাতৃক মোৰ সজোৱা হৈছে সন্দেহযুক্ত ভোটাৰ যদিও পিতৃ-মাতৃ তাইৰ নিঃসন্দেহে ভাৰতীয়
ইচ্ছা কৰিলেই তুমি মোক হত্যা কৰিব পাৰা, জ্বলাই দিব পৰা মোৰ খেৰৰ পঁজা, খেদি দিব পাৰা মোক মোৰেই গাঁৱৰ পৰা, কাঢ়ি নিব পাৰা মোৰ সেউজী পথাৰ মোৰ বুকুৰ ওপৰেৰে চলাব পাৰা তোমাৰ বুলড্জাৰ তোমাৰ বুলেটে বুকুখন মোৰ কৰিব পাৰে থকাসৰকা (তোমাৰ এই কাৰ্যৰ বাবে তুমি কোনো স্তিও নোপোৱা) যুগ-যুগান্তৰ তোমাৰ অত্যাচাৰ সহ্য কৰি ব্ৰহ্মপুত্ৰৰ চৰত বাস কৰা মই এজন মিঞা মোৰ দেহা হৈ পৰিছে নিগ্ৰো কলা মোৰ চকুযুৰি অঙঠাৰ দৰে ৰঙা সাৱধান! মোৰ দুচকুত জমা হৈ আছে যুগ যুগান্তৰৰ বঞ্চনাৰ বাৰুদ আঁতৰি যোৱা, নতুবা অচিৰেই পৰিণত হ’বা মূল্যহীন ছাইত!
Write Down ‘I am a Miyah’ Hafiz Ahmed, 2016 trans. Shalim M. Hussain
Write Write Down I am a Miya My serial number in the NRC is 200543 I have two children Another is coming Next summer. Will you hate him As you hate me?
write I am a Miya I turn waste, marshy lands To green paddy fields To feed you. I carry bricks To build your buildings Drive your car For your comfort Clean your drain To keep you healthy. I have always been In your service And yet you are dissatisfied! Write down I am a Miya, A citizen of a democratic, secular, Republic Without any rights My mother a D voter, Though her parents are Indian.
If you wish kill me, drive me from my village, Snatch my green fields hire bulldozers To roll over me. Your bullets Can shatter my breast for no crime.
Write I am a Miya Of the Brahamaputra Your torture Has burnt my body black Reddened my eyes with fire. Beware! I have nothing but anger in stock. Keep away! Or Turn to Ashes.
]
[Mahmoud Darwish Transcripts (Arabic and English):
سجِّل أنا عربي ورقمُ بطاقتي خمسونَ ألفْ وأطفالي ثمانيةٌ وتاسعهُم.. سيأتي بعدَ صيفْ! فهلْ تغضبْ؟ سجِّلْ أنا عربي وأعملُ مع رفاقِ الكدحِ في محجرْ وأطفالي ثمانيةٌ أسلُّ لهمْ رغيفَ الخبزِ، والأثوابَ والدفترْ من الصخرِ ولا أتوسَّلُ الصدقاتِ من بابِكْ ولا أصغرْ أمامَ بلاطِ أعتابكْ فهل تغضب؟ سجل أنا عربي أنا اسم بلا لقبِ صَبورٌ في بلادٍ كلُّ ما فيها يعيشُ بفَوْرةِ الغضبِ جذوري قبلَ ميلادِ الزمانِ رستْ وقبلَ تفتّحِ الحقبِ وقبلَ السّروِ والزيتونِ .. وقبلَ ترعرعِ العشبِ أبي.. من أسرةِ المحراثِ لا من سادةٍ نُجُبِ وجدّي كانَ فلاحاً بلا حسبٍ.. ولا نسبِ! يُعَلّمني شموخَ الشمسِ قبلَ قراءةِ الكتبِ وبيتي’ كوخُ ناطورٍ منَ الأعوادِ والقصبِ فهل تُرضيكَ منزلتي؟ أنا اسم بلا لقبِ! سجلْ أنا عربي ولونُ الشعرِ.. فحميٌّ ولونُ العينِ.. بنيٌّ وميزاتي: على رأسي عقالٌ فوقَ كوفيّه وكفّي صلبةٌ كالصخرِ... تخمشُ من يلامسَها وعنواني: أنا من قريةٍ عزلاءَ منسيّهْ شوارعُها بلا أسماء وكلُّ رجالها في الحقلِ والمحجرْ فهل تغضبْ؟ سجِّل! أنا عربي سلبتُ كرومَ أجدادي وأرضاً كنتُ أفلحُها أنا وجميعُ أولادي ولم تتركْ لنا.. ولكلِّ أحفادي سوى هذي الصخورِ... فهل ستأخذُها حكومتكمْ.. كما قيلا!؟ إذنْ سجِّل.. برأسِ الصفحةِ الأولى أنا لا أكرهُ الناسَ ولا أسطو على أحدٍ ولكنّي.. إذا ما جعتُ آكلُ لحمَ مغتصبي حذارِ.. حذارِ.. من جوعي ومن غضبي!!
Identity Card Mahmoud Darwish, 1964 trans. Denys Johnson-Davies
Put it on record. I am an Arab
And the number of my card is fifty thousand I have eight children And the ninth is due after summer. What's there to be angry about?
Put it on record. I am an Arab
Working with comrades of toil in a quarry. I have eight children For them I wrest the loaf of bread, The clothes and exercise books From the rocks And beg for no alms at your door, Lower not myself at your doorstep. What's there to be angry about?
Put it on record. I am an Arab.
I am a name without a title, Patient in a country where everything Lives in a whirlpool of anger. My roots Took hold before the birth of time Before the burgeoning of the ages, Before cypress and olive trees, Before the proliferation of weeds.
My father is from the family of the plough Not from highborn nobles.
And my grandfather was a peasant Without line or genealogy.
My house is a watchman's hut Made of sticks and reeds.
Does my status satisfy you? I am a name without a surname.
Put it on record. I am an Arab.
Color of hair: jet black. Color of eyes: brown. My distinguishing features: On my head the `iqal cords over a keffiyeh Scratching him who touches it.
My address: I'm from a village, remote, forgotten, Its streets without name And all its men in the fields and quarry. What's there to be angry about?
Put it on record. I am an Arab.
You stole my forefathers' vineyards And land I used to till, I and all my children, And you left us and all my grandchildren Nothing but these rocks. Will your government be taking them too As is being said?
So! Put it on record at the top of page one: I don't hate people, I trespass on no one's property.
And yet, if I were to become hungry I shall eat the flesh of my usurper. Beware, beware of my hunger And of my anger!
]
#it speaks!#re: the tag on my last reblogged post. decided to make that point its own post!#this is long obviously and im employing proper capitalization for ease of reading#obligatory im monolingual disclaimer & cant vouch for translation quality; i chose the johnson-davies translation because ->#<- it is the one i see most commonly spread. i take responsibility for any deficiencies.#going to use some tags because im personally interested in this poetic movement & connection & maybe other people will be too!#palestine#palestinian poetry#assam#miya poetry#political poetry#poetry
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
Literature produced in the ex-colonial countries but produced directly in languages which had been imported initially from Europe provides one kind of archive for the metropolitan university to construe the textual formation of ‘Third World Literature’; but this is not the only archive available, for the period after decolonization has also witnessed great expansion and consolidation of literary traditions in a number of indigenous languages as well [...] Not much of this kind of literature is directly available to the metropolitan literary theorists because, erudite as they usually are in metropolitan languages, hardly any of them has ever bothered with an Asian or African language. But parts and shades of these literatures also become available in the West, essentially in the following three ways. By far the greater part of the archive through which knowledge about the so-called Third World is generated in the metropolises has traditionally been, and continues to be, assembled within the metropolitan institutions of research and explication, which are characteristically administered and occupied by overwhelmingly Western personnel. Non-Western individuals have also been employed in these same institutions – more and more so during the more recent, post-colonial period, although still almost always in subordinate positions. The archive itself is dispersed through myriad academic disciplines and genres of writing – from philological reconstruction of the classics to lowbrow reports by missionaries and administrators; from Area Study Programmes and even the central fields of the Humanities to translation projects sponsored by Foundations and private publishing houses alike – generating all kinds of classificatory practices. A particularly large mechanism in the assembly of this archive has been the institutionalized symbiosis between the Western scholar and the local informant, which is frequently re-enacted now – no doubt in far more subtle ways –between the contemporary literary theorist of the West, who typically does not know a non-Western language, and the indigenous translator or essayist, who typically knows one or two. This older, multidisciplinary and somewhat chaotic archive is greatly expanded in our own time, especially in the area of literary studies, by a developing machinery of specifically literary translations – a machinery not nearly as highly developed as the one that exists for the circulation of texts among the metropolitan countries themselves, but not inconsiderable on its own terms. Apart from the private publishing houses and the university presses which may publish such translations of their own volition or under sponsorship programmes, there are state institutions such as the Sahitya Akademi in India, as well as international agencies such as UNESCO, not to speak of the American ‘philanthropic’foundations such as the Rockefeller-funded Asia Society, which have extensive programmes for such publications. Supplementing these translations are the critical essay and its associated genres, usually produced by an indigenous intellectual who reads the indigenous language but writes in one of the metropolitan ones. Some of this kind of writing becomes available in the metropolises, creating versions and shadows of texts produced in other spaces of the globe, but texts which frequently come with the authority of the indigenous informant.
Aijaz Ahmed, In Theory: Nations, Classes, Literatures
175 notes
·
View notes
Text
Venkatasuchus: Aetosaur from India
Once more I come bearing croc news. For the second time this year we are getting a new type of aetosaur, you know, those weird stem-crocodiles that somewhat converged with ankylosaurs? Yeah those guys. Much like Kryphioparma from just a few months ago, this new genus Venkatasuchus is a member of the Typothoracinae and known only from osteoderms. Thankfully, in the case of Venkatasuchus a lot more of them at least.

I mean sure 8 associated osteoderms plus the connected lateral elements is not that much, but it sure beats the few remains of Kryphioparma.
Anyhow, Venkatasuchus is from the middle Norian to Rhaetian stages of the Triassic of India, more specifically the Lower Dharmaram Formation in the east of the subcontinent. This is actually quite significant as aetosaurs are generally rare in Gondwanan parts of the world and the Dharmaram Formation actually has two: Venkatasuchus and an as of yet undescribed desmatosuchine. Furthermore, the formation actually represents a melting pot of Laurasian and Gondwanan fauna. The aetosaurs and phytosaurs are of Laurasian origin, but the dinosaurs of the formation are Gondwanan lineages.


Much to my surprise, there is ALREADY an illustration of this guy online courtesy of Scott Reid on Twitter, fantastic art, love how he cheekily hides the head and focuses on the armour.

Venkatasuchus - Wikipedia
Of course I jumped at the opportunity to write its wiki page, so far I do believe I managed to cover every new genus published this year.
#aetosaur#aetosauria#aetosaurinae#typothoracinae#paratypothoracini#venkatasuchus#triassic#india#palaeoblr#paleontology#prehistory#pseudosuchia#stem croc#croctober
140 notes
·
View notes
Text
Originally posted Jan 2023.
The medical community and the media hang their hats on the use of ‘double-blind, placebo-controlled, peer-reviewed studies published in legacy journals such as The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) and the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA). In a future substack, I will go into detail about the fallacies, and even the scam, of peer review and why it should not be held out as sacrosanct.
For today’s discussion, let’s examine why all vaccine research should be questioned. Yes, ALL of it. If you read enough studies, you’ll see the patterns described below. For this substack, I’ll use this study on the safety of hepatitis B vaccination in children in India as an example. The vaccine used, Revac-B, contained both 0.5mg of aluminum and 0.05 mg of thimerosal, considered to be safe.
1. Vaccine trials can be quite small and include only healthy children.
Every study begins with ‘selection criteria’ that describe including only healthy individuals. This is from the hepatitis B study example:
All 60 subjects included in the study were in good health and had a negative history of hematological, renal, hepatic, or allergic diseases. All were screened and found to have normal blood panels, including normal liver enzymes.
When a vaccine trial has been completed and the vaccine is approved for use by the FDA, the vaccine is recommended for ALL children, regardless of their health condition, family history, or genetics. In fact, the new shot is most ardently pushed on children with underlying health concerns, such as seizure disorders, cardiac anomalies, and conditions such as cystic fibrosis or Down’s syndrome. These children become the next round of experimentation because the vaccines were never tested for safety on these groups and others.
2. Vaccine studies follow side effects for a short period of time.
Most clinical trials monitor for side effects for a paltry 21 days, often less. In some studies, such as in the example we are using, children were monitored for 5 days by study monitors and 5 days by cards given to parents. If no reactions occur, the shot is deemed to be ‘safe.’
However, it can take weeks to months for immune and neurological complications to appear. These arbitrary deadlines, allowed by the FDA, prohibit making the connection between vaccines with chronic health disorders. If an illness emerges later, of course, the doctors will say it has nothing to do with the vaccine.
3. Most vaccine safety studies do not use a true placebo.
The gold standard in medical research is the "placebo-controlled" trial. A placebo is an inactive or inert substance, such as a sugar pill or a shot of saline. In the trial, the placebo is given to one group, while the treatment group is given the experimental product. The placebo arm is used to ‘blind’ the study so the investigator doesn’t know if the subject received the Real Thing or the Inert Substance to minimize interpretation bias.
When reading a published vaccine trial, the substance used as the placebo is often not identified; it is simply called ‘placebo.’ For example, in this study for a new hepatitis B vaccine to treat chronic hepatitis B, the word ‘placebo’ is used 22 times, but we don’t know what placebo was used.
And that’s a problem. The substance used as a ‘placebo’ is often not inert; it may even may be another vaccine. For example, I remember reading a study where the meningitis C vaccine was used as a placebo because it was considered to be non-immunogenic and non-reactive. Or, in the instance of the Gardasil (HPV) vaccine, the ‘placebo’ was an injection of aluminum.
All studies for the Gardasil vaccine were said to be placebo-controlled and the total population that received a placebo included 9,701 subjects. The placebo was an aluminum adjuvant in all studies except study 018 (pre-/adolescent safety study), which used a non-aluminum-containing placebo [and we don’t know what that placebo was]
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Picture of Dorian Gray is interesting. Oscar Wilde was a part of aestheticism, or "art for art's sake." This was pretty big because in Victorian England, art was often meant to serve a function; this isn't a new idea. Often, the function was to be didactic, or to prescribe a moral lesson.
That said, I would argue that there is a theme in Dorian Gray about Victorian standards of beauty. There is a strong irony in Dorian being the epitome of (racist, white supremacist) beauty standards: fair skin ("looks as if he was made out of ivory and rose leaves"); "crisp gold hair"; "frank" blue eyes. The irony is because Victorians associated being beautiful with being a good person and being outside this standard with being a bad person. They often used phrenology and physiognomy (most evident in Stoker's description of the Count in Dracula) to tell the reader whether someone is good or bad. And of course, using someone's facial features and the size and shape of one's forehead, nose, etc. to determine whether someone is good or bad has its roots in racism, xenophobia, and antisemitism.
Therefore, there is a disruption of Victorian preconceptions when Dorian fixates on maintaining his youth and beauty and is assumed to be virtuous because of his appearance when he is a horrible, callous person.
That is to say that I think a take on Dorian Gray that explores the beauty/fashion industry would work very well, given how so many of these companies perpetuate unrealistic and negative standards. Dove was being applauded for its body positivity in an ad a while ago, alongside its insistence that it wants to promote self-esteem and good body image, but they reject potential models with any acne or too many freckles. While Dove speaks about being inclusive and promoting women of color, so many of these companies, including Dove, sell skin-lightening creams in countries like India; they promote the idea that light skin is more attractive than dark skin. Unfortunately, there are horrible ways the modern fashion and beauty industries mirror imperialistic Victorian values that, with the right creators, could be explored well in a contemporary Dorian Gray adaptation.
Unfortunately, I was already cynical about any and all Netflix book adaptations, and, regarding the author's biography and the book's themes, I feel like Dorian Gray cannot be removed from its queerness, despite statements such as the PinkNews article, which says, "While The Picture of Dorian Gray isn't explicitly queer, given that it was first published in 1890..."
I would take umbrage with the author's definition of "explicitly queer," given that the book was submitted as evidence of Wilde's "gross indecency" in the counter lawsuit that sent him to prison and shortened his life through years of hard labor and an injury he sustained that later developed into fatal meningitis. Despite Wilde's edits to "restrain" the book's queerness, it was explicit enough to be used as evidence to prove Wilde's homosexuality. I think it's a mistake that highly limits the history of queer art to reduce "explicitly queer" to only depictions of kissing and sex.
Anyway, those are my rambling thoughts about the Dorian Gray Netflix adaptation. Besides the brother thing, I was already skeptical because it's Netflix...
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

SWATI
Swati Nakshatra, symbolized by a sword or a blade of grass swaying in the wind, epitomizes a sense of autonomy and fluidity in life's journey. Governed by Vayu, the divine force of wind and vitality, Swati individuals possess an innate inclination towards independence and innovation.
With a focus on material attainment (artha), they navigate life's challenges with a calm and composed demeanor, often excelling in pursuits that require both creativity and practicality.
However, Swati's connection to Rahu, the ruling planet of the nakshatra, adds a layer of complexity. Rahu's influence imbues Swati natives with a sense of restlessness and a tendency towards unconventional thinking. This can manifest as a propensity for indecision and a desire to explore various options before committing to a course of action.
Despite these challenges, Swati individuals harness their determination and discernment, much like the sword symbol of this nakshstra, to cut through obstacles and carve out their paths with precision. They possess a natural charm and sophistication, drawing upon their Venusian influence to navigate social interactions with ease.
The association of Swati with Saraswati, the revered goddess of learning and wisdom, underscores its intellectual acumen and gift for effective communication. Swati natives naturally gravitate towards pursuits that stimulate their minds, displaying a keen curiosity and receptivity to new ideas.
In essence, Swati Nakshatra embodies a harmonious balance between pragmatism and aesthetic sensibility. Its airy nature, combined with the influence of Venus and Rahu, propels individuals towards continuous growth and adaptation, as they strive to find equilibrium between material success and inner fulfillment.
REFERENCES
Sutton, Komilla. Nakshatras: The Stars Beyond the Zodiac. The Wessex Astrologer, 2014.
Tridevi, Prash. The Book of Nakshatras: A Comprehensive Treatise on the 27 Constellations. Sagar Publications, 2005.
Pijan, Barbara. Barbara Pijan Lama (year unknown) . Available at:
https://barbarapijan.com/bpa/Nakshatra_radical/15swati.htm
Holliday, Mike. Mike’s Sleeping Dog website (year unknown). Available at:
https://mikessleepingdog.com/2022/02/05/15-swati-nakshatra/?amp#
Harness, Dennis M.. Nakshastras: The Lunar Mansions of Vedic Astrology. India, Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Pvt. Limited, 2004.
Nakti, Claire. Nakshatra Feature Focus: Swati "Bug Pretty" Eyes (2023)
Available at: https://www.clairenakti.com/post/nakshatra-feature-focus-swati-bug-pretty-eyes
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this National Geographic story:
A 14-year-old boy who went swimming in a pond in India’s sweltering heat. A 13-year-old girl who bathed in a pool during a school excursion, and a five-year-old girl who took a dip in a river near her home. The three children lived in different parts of the southern Indian state of Kerala. Yet they have something in common ⸺all of them succumbed to a brain infection, Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM), caused by a tiny organism found in warm freshwaters and poorly maintained swimming pools. About a dozen others have been undergoing treatment in India, one of whom, a 27-year-old man, has also succumbed.
Although rare, PAM is a deadly infection with a worldwide occurrence. It is caused by Naegleria fowleri, also known as the "brain-eating amoeba”, as it infects the brain and destroys brain tissue. At least 39 countries have reported such infections so far, and the rate of infections is increasing by 4.5 percent every year. In Pakistan alone, 20 deaths are reported every year due to the disease, and in 2024, infections have been reported in India, Pakistan, and Israel. N. fowleri was also detected at a popular freshwater swimming spot in Western Australia and hot springs in the U.S’s Grand Teton National Park.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the majority of global case exposures⸺85 percent⸺have been reported during warm, hot, or summer seasons. Several studies have also observed that changes in temperature and climate may further drive a global increase in PAM incidence. A study published in May last year found that PAM infections are on the rise in the northern U.S. "N. fowleri is expanding northward due to climate change, posing a greater threat to human health in new regions where PAM has not yet been documented," the study noted.
Yun Shen, an assistant professor of chemical and environmental engineering at the University of California, Riverside, says that she considers PAM as “a potential emerging medical threat worldwide”. She explains that while warmer temperatures are likely to facilitate the survival and growth of N. fowleri, the risk of exposure may also increase as people indulge in more water-based recreational activities in hotter weather.
N. fowleri is found in warm, untreated freshwater, soil, and dust, says Karen Towne, a clinical associate professor of nursing at the University of Mount Union in Ohio, who co-authored a 2023 study on how the amoeba poses “a new concern for northern climates”. She adds that so far, PAM infections have typically occurred in cases involving swimming, splashing, and submerging one’s head in freshwater lakes, ponds, hot springs, and reservoirs. Meanwhile, less common routes of transmission have included warm hose water, a lawn water slide, splash pad use, and exposure of the nasal membrane to tap water from private well systems.
“Epidemiologically, most cases have occurred in healthy children and young adults⸺more males than females⸺who have had recent contact with untreated fresh water,” Towne told National Geographic in an email interview.
According to Barbara Polivka, an associate dean of research at the University of Kansas School of Nursing, who co-authored the study with Towne, N. fowleri enters the nose via contaminated water, crosses the nasal membrane, and follows the olfactory nerve into the brain, where it incubates for an average of five days. “PAM begins with rapid onset of severe frontal headache, fever, nausea and vomiting, which worsen into stiff neck, altered mental status, hallucinations, coma, and death,” says Polivka.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
At the time, [Ian] Stevenson was Chair of the Department of Psychiatry at the University of Virginia Medical School. During his more than half-century at the University of Virginia, Stevenson carried out pioneering work in the empirical investigation of the mind-body connection, focusing on phenomena suggesting that contemporary scientific hypotheses concerning the nature of mind, and the mind’s relation to matter, may be seriously incomplete.
Stevenson authored a dozen books and more than two hundred scientific publications related to this work. Stevenson was a meticulous scientist and conservative in his interpretation of data. At the same time, he was a true visionary, and courageous in his study of phenomena that lie outside the current scientific mainstream. Under Stevenson’s leadership, DOPS became the largest and longest-running university-based group in the United States devoted exclusively to empirical investigation of phenomena that are not easily encompassed by the current paradigm in the biophysical sciences for understanding the mind. This paradigm maintains that consciousness is entirely generated by, or emerges from, the physical processes of the brain and body, and can in no way be more than that.
[...]
In 1975, Stevenson began a four-volume series of books called Cases of the Reincarnation Type. The different volumes included carefully documented cases from India, Sri Lanka, Lebanon and Turkey, and Thailand and Burma. When the first volume was published, the book review editor of JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association, wrote: “In regard to reincarnation he has painstakingly and unemotionally collected a detailed series of cases from India, cases in which the evidence is difficult to explain on any other grounds.”
[...]
Over the years, Stevenson studied cases of children born with birthmarks or defects that corresponded to wounds (usually the fatal wounds) suffered by the deceased individuals whose lives the children appeared to remember. He went to great lengths to verify that the birthmarks or birth defects did in fact match the previous wounds. He always tried to obtain autopsy reports if they were available, along with medical records or police reports. If no written records were available, he would elicit eyewitness testimony about the wounds.
For many years, he put off publishing reports as his collection continued to grow. Finally, in 1997, Stevenson produced Reincarnation and Biology: A Contribution to the Etiology of Birthmarks and Birth Defects, a 2,200-page, two-volume collection of over two hundred such cases.
He also wrote a shorter synopsis of that work, entitled Where Reincarnation and Biology Intersect. In these books, he included numerous pictures of birthmarks and defects that were often highly unusual. The cases included a girl born with markedly malformed fingers who remembered the life of a man whose fingers were chopped off; a boy with only stubs for fingers on his right hand who remembered the life of a boy in another village who lost the fingers of his right hand in a fodder-chopping machine; and a girl who remembered the life of a man who underwent skull surgery. She had what Stevenson called the most extraordinary birthmark he had ever seen: a three-centimeter wide area of pale, scar-like tissue that extended around her entire head.
He reported that in eighteen cases in which the previous person was shot, the child was born with double birthmarks, ones corresponding to both the entrance and the exit wound on the previous person’s body.
-- David E. Presti (ed.), Mind Beyond Brain: Buddhism, Science, and the Paranormal
9 notes
·
View notes